If you suspect that you have this disease, and you do not know what psoriasis looks like and how to treat it, you should learn more about this disease and visit a dermatologist immediately.
What does psoriasis look like in the initial stage: symptoms, photos
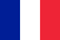
For psoriasis at any stage, skin rashes are characteristic. From the very beginning of its development, the disease manifests itself in various ways. In some cases, it begins actively, develops quickly, in others, small and slow manifestations. In any case, in the absence of medical care, the disease progresses and affects more and more areas of the skin.
The initial stage of the disease in the form of small rashes (papules) can complicate the diagnosis. Over time, the rash grows, merging into plaques covered with horny scales. It is very important to diagnose psoriasis in the early stages so that treatment can begin immediately. The outcome of treatment will be long-term remission, in some cases 3-4 years.
Psoriasis is characterized by the following places on our skin:
- small part of the back
- knees and elbows
- inguinal folds
- head
- lower legs
The disease has several forms, each of which has its own characteristics. Depending on where and how exactly the papules appear, it will depend on what kind of psoriasis the dermatologist diagnoses.
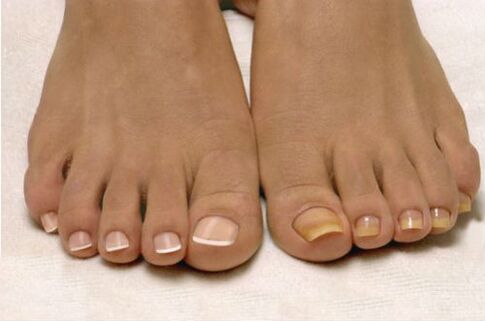
The skin rash is unhealthy in any case, but with the following symptoms it is most likely associated with psoriasis:
- The spots are red, have a slight protrusion and are covered with scales (dead cells) that peel off.
- Plaques appear anywhere, more often in the knee and elbow area. Sometimes it itches.
- Nails peel, deform.
- On the feet, palms, painful blisters that may itch.
What are the forms of psoriasis
The most common form is plaque psoriasis. It is also commonly referred to as plain or vulgar. In all cases, 90% of diseases of this form occur.
Psoriasis vulgaris is characterized by raised red plaques with gray or white scales. Infected skin is inflamed, easily injured and bleeds when the scales come off. Over time, plaques on the skin grow, uniting in large areas because. called "paraffin lakes".
Named the other way around, psoriasis of the flexion surfaces are smooth, slightly protruding red spots that barely peel off. Localization of spots mainly in the folds of the skin: groin and armpits, external genitalia, folds below the abdomen and mammary glands (in obesity).
Spread to other areas of the skin is minimal, but the treatment of this form is complicated due to natural friction when moving, sweating. Inverse psoriasis, if left untreated, can be accompanied by streptococcal pyoderma or fungal diseases.
Guttate psoriasis is not so common, but is a complication after streptococcal infections. It is characterized by small lesions in the form of drops. Another recognizable feature of gut psoriasis is the color of psoriatic plaques, ranging from red to purple. The affected area is extensive, most often the hips, it can also appear on other parts of the skin.
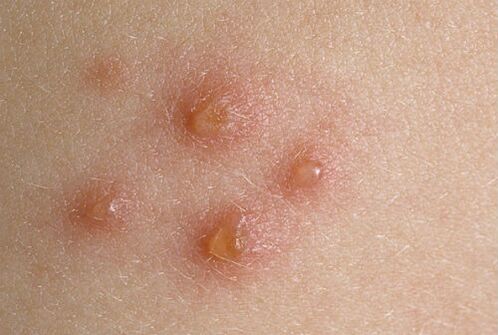
One of the most severe forms is attributed to pustular psoriasis. Its symptoms are blisters (clear) with clear fluid. The skin under and around them is hot and inflamed. When the blisters become infected, the clear liquid fills with pus, peels easily, but is difficult to treat. Place of localization - lower legs and forearms.
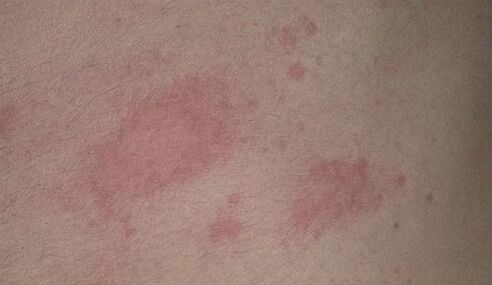
Psoriatic onychodystrophy develops on the nails of the hands and feet. This shape leads to changes in the nails. They may change color, dots or transverse lines appear. More severe forms are characterized by delamination or complete loss of the nail.
Psoriatic arthritis accounts for only 10% of cases. This form affects the joints and connective tissues. It mostly affects the fingers. In some cases, psoriasis can affect the hip, knee and spine. This leads to psoriatic spondylitis. In severe forms of psoriatic spondylitis, the patient cannot move independently.
Erythrodermic psoriasis is characterized by large areas of inflammation, it can occur against the background of worsening psoriasis vulgaris. In large foci of inflammation, it can be fatal, because the natural ability to thermoregulate is lost.
Development of psoriasis
Psoriasis can affect different parts of the body, with different symptoms. Let's consider different cases.
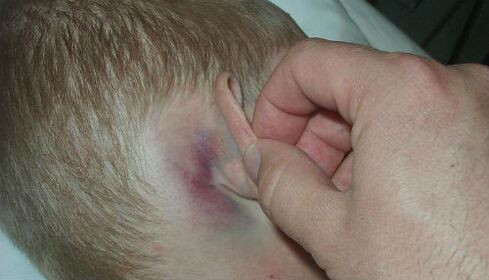
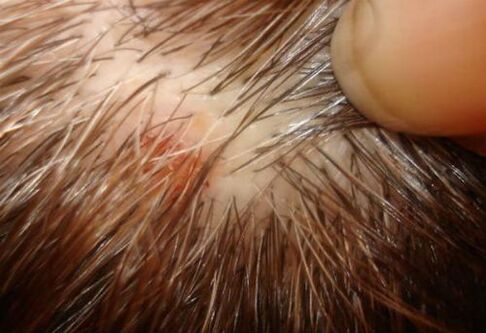
It appears on the scalp, behind the ears. Papules in these places itch, may be cracked, wet.
On the body
The nature of the plaques on the body and their intensity depend on the form of psoriasis. The initial psoriasis on the body manifests itself in different ways: from individual rashes to large areas.
On your hands
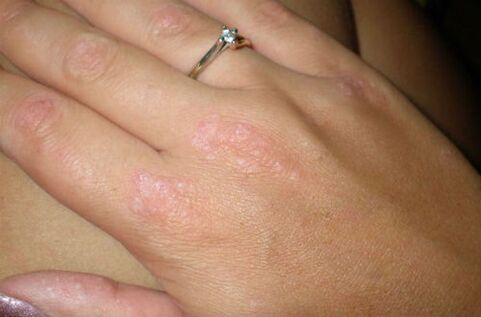
Plaques first appear on the elbows, forearms, and then spread to the palms and fingers.
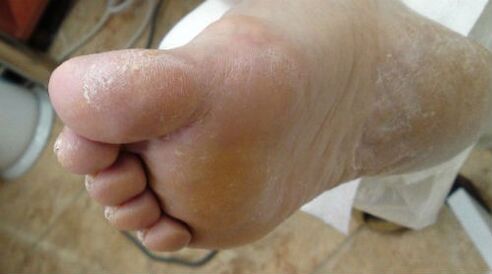
On your feet
The first manifestations begin on the knees or feet, advancing to other areas.
On the elbows and knees
Psoriasis in these areas looks like a red, scaly rash, the skin in these areas is rough.
On the palms
Plaques in these places occur when other areas are infected. It is dangerous that if left untreated, psoriatic arthritis can develop.
On the face
It rarely occurs in this area. It affects the area of nasolabial folds, eye area, cheeks. Sometimes it spreads to the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks.
On the nails
It can be mixed with the fungus in appearance, starting with spots, furrows and ending with a complete peeling.
Onset of psoriasis in children
The pediatric version of the disease, especially in infants, is symptomatic and can often be confused with diaper rash or diaper dermatitis. After that, peeling of the upper layers of the skin occurs in places of redness, followed by severe itching. It is extremely important that the disease is not brought to this stage, because it brings discomfort to infants.
Also, psoriasis can be expressed in a child on the head, such cases are characterized by crusts, when peeled, small wounds remain. In any case, you should not treat your child alone just because you know what psoriasis looks like to avoid complications of the disease.
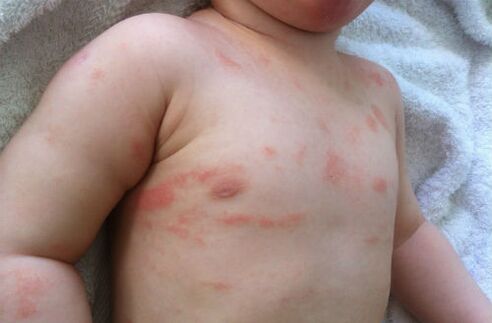
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis is not contagious, scientists have identified several reasons for its appearance. In addition, it has been proven that psoriasis in childhood, ie up to 10 years, occurs due to genetics, ie. there were relatives in the family with a similar disease. Subsequent cases are associated with other causes.
If we combine all the factors that cause psoriasis, then the following may be to blame for its manifestation:
- alcohol abuse
- genetic inheritance
- excessive hygiene
- dry skin
- stress
- taking medication
- staphylococcal and fungal infections
Treatment in the initial phase
If you have been diagnosed with psoriasis, it is essential that you stick to a diet and start treatment as soon as possible, because psoriasis is initially easier and faster to cure. Until psoriasis plaques begin to grow, a dermatologist will most likely recommend an external treatment with the following ointments:
- Naphthalene ointment. It is prescribed in the initial stages and healing. Relieves inflammation and soothes itching.
- Sulfur-tar ointment. Relieves inflammation, suitable only for "dry" forms of psoriasis. Ointment should not be applied to the face.
- Salicylic ointment. It contains salicylic acid, thanks to which the shells soften and are easily removed.
medicines
In addition to fats, treatment consists of physiotherapy procedures (electro-sleep, magnetotherapy, ultraviolet radiation, etc. ), drugs, vitamin complexes. The complete complex is intended for cases with progressive and severe forms.
Prescribing drugs is done only after the examination and, as a rule, includes a certain group of drugs:
- antihistamines,
- diuretics,
- immunomodulators,
- immunosuppressants,
- antidepressants,
- NSAIDs (a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs),
- enterosorbents,
- vitamin complexes.
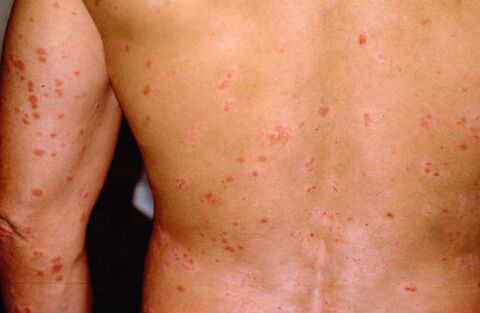
Folk remedies
Traditional treatment, especially in the primary stages, can be combined with traditional treatment recipes. One of these recipes suggests the use of celandine juice. It is necessary to smear the spots with fresh juice all summer, then by the end of the summer the plaques will be significantly reduced. If you perform the procedures for three summers in a row, the stains should disappear forever.
For early psoriasis, the following recipe is suitable - beaten egg ointment. Preparation is simple: 2 eggs, 1 tbsp. l. vegetable oil, whisk well and add 0, 5 tbsp. l. acetic acid. This mixture can be stored, but only in a closed container and in a dark place. Use as follows: pat the areas affected by psoriasis at night, daily.
You can also prepare an ointment based on fat, which greatly helps in the treatment of psoriasis. It is necessary to take 300 g of fat, 2 chicken yolks and 100 g of linden honey. Use within two weeks. To lubricate sore spots, leave for 2 hours 3 times a day, then rinse. After two weeks, prepare another batch by adding 2 tbsp. l. celandine powder. This composition is designed for one hour.
In addition to ointments for psoriasis, you can also take therapeutic baths with the addition of sea salt or, for example, walnuts. It is useful to take such a bath not only in the early stages, but also during the worsening of the disease. For one bath, it is necessary to prepare leaves or shells, about 400 g. Pour boiling water over them, leave for 10 minutes, then strain. The filtered solution is intended for therapeutic baths, it must be taken within half an hour.
How to prevent psoriasis
It is known why plaque psoriasis occurs, but it is not fully understood why it takes certain forms. The disease can manifest after stress, disturbances in the immune system, past infections or at the genetic level.
To protect yourself from relapse, you need to give up bad habits. Also, doctors advise you to moisturize dry skin well and, if possible, avoid burns, hypothermia and skin injuries. In addition, you should be careful when taking antibiotics, vaccines and beta-blockers, because they can cause worsening.
Avoiding infections, a healthy lifestyle, not overloading and avoiding stressful situations and worries - these measures will help in some way in the prevention of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a disease that needs treatment, but can be confused with similar skin conditions. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself based on photography, and even more, prescribe treatment without the necessary knowledge.